Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Efficacy and Safety of the New Appetite Suppressant, Liraglutide: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Shinje Moon, Jibeom Lee, Hye Soo Chung, Yoon Jung Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang-Myung Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):647-660. Published online June 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.934

- 6,199 View
- 302 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is a chronic disease associated with metabolic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved liraglutide as an anti-obesity drug for nondiabetic patients in 2014, it has been widely used for weight control in overweight and obese people. This study aimed to systematically analyze the effects of liraglutide on body weight and other cardiometabolic parameters.
Methods
We investigated articles from PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library to search randomized clinical trials that examined body weight changes with liraglutide treatment.
Results
We included 31 studies with 8,060 participants for this meta-analysis. The mean difference (MD) between the liraglutide group and the placebo group was −4.19 kg (95% confidence interval [CI], −4.84 to −3.55), with a −4.16% change from the baseline (95% CI, −4.90 to −3.43). Liraglutide treatment correlated with a significantly reduced body mass index (MD: −1.55; 95% CI, −1.76 to −1.34) and waist circumference (MD: −3.11 cm; 95% CI, −3.59 to −2.62) and significantly decreased blood pressure (systolic blood pressure, MD: −2.85 mm Hg; 95% CI, −3.36 to −2.35; diastolic blood pressure, MD: −0.66 mm Hg; 95% CI, −1.02 to −0.30), glycated hemoglobin (MD: −0.40%; 95% CI, −0.49 to −0.31), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (MD: –2.91 mg/dL; 95% CI, −5.28 to −0.53; MD: −0.87% change from baseline; 95% CI, −1.17 to −0.56).
Conclusion
Liraglutide is effective for weight control and can be a promising drug for cardiovascular protection in overweight and obese people. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacotherapy for obesity: moving towards efficacy improvement
Walmir Coutinho, Bruno Halpern
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physiopathology and Treatment of Obesity and Overweight: A Proposal for a New Anorectic
Bruno Silvestrini, Mauro Silvestrini, Mayank Choubey
Journal of Obesity.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Side effect profile of pharmacologic therapies for liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yilin Li, Rong Lei, Honglin Lei, Qin Xiong, Fengjiao Xie, Chengjiao Yao, Peimin Feng
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 35(1): 1. CrossRef - Recommendations for the prevention and management of obesity in the Iraqi population
Hussein Ali Nwayyir, Esraa Majid Mutasher, Osama Mohammed Alabid, Muthana Abdulrazzaq Jabbar, Wefak Hasan Abdulraheem Al-Kawaz, Haider Ayad Alidrisi, Majid Alabbood, Muhammed Chabek, Munib AlZubaidi, Lujain Anwar Al-khazrajy, Ibtihal Shukri Abd Alhaleem,
Postgraduate Medicine.2023; 135(5): 425. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, in individuals with obesity in clinical practice
Juyoung Shin, Raeun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 49. CrossRef - The effects of subcutaneous Tirzepatide on obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta‐regression analysis of randomized controlled trials
Pejman Rohani, Nasser Malekpour Alamdari, Seyedeh Elaheh Bagheri, Azita Hekmatdoost, Mohammad Hassan Sohouli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of liraglutide for weight management in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hao Gou, Yiman Zhai, Junjun Guo
European Journal of Pediatrics.2023; 182(11): 5095. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: a meta-analysis
Ping Zhong, Hai Zeng, Miaochun Huang, Wenbin Fu, Zhixia Chen
Endocrine.2022; 75(3): 718. CrossRef - Pharmacological profile of once-weekly injectable semaglutide for chronic weight management
David C. W. Lau, Rachel L Batterham, Carel W. le Roux
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 15(3): 251. CrossRef - Pharmacological Management of Obesity: A Century of Expert Opinions in Cecil Textbook of Medicine
Peter Manu, Cristina-Mihaela Lăcătuşu, Liliana M. Rogozea, Simona Cernea
American Journal of Therapeutics.2022; 29(4): e410. CrossRef - GLP-1 agonists: superior for mind and body in antipsychotic-treated patients?
Katerina Horska, Jana Ruda-Kucerova, Silje Skrede
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 33(9): 628. CrossRef - Targeting skeletal muscle mitochondrial health in obesity
Chantal A. Pileggi, Breana G. Hooks, Ruth McPherson, Robert R.M. Dent, Mary-Ellen Harper
Clinical Science.2022; 136(14): 1081. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Loss Cause as per the Side Effect of Liraglutide
Jin Yu, Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyung Cho, Hun-Sung Kim, Heng Zhou
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Pharmacotherapy for obesity: moving towards efficacy improvement

Special Article
- Miscellaneous
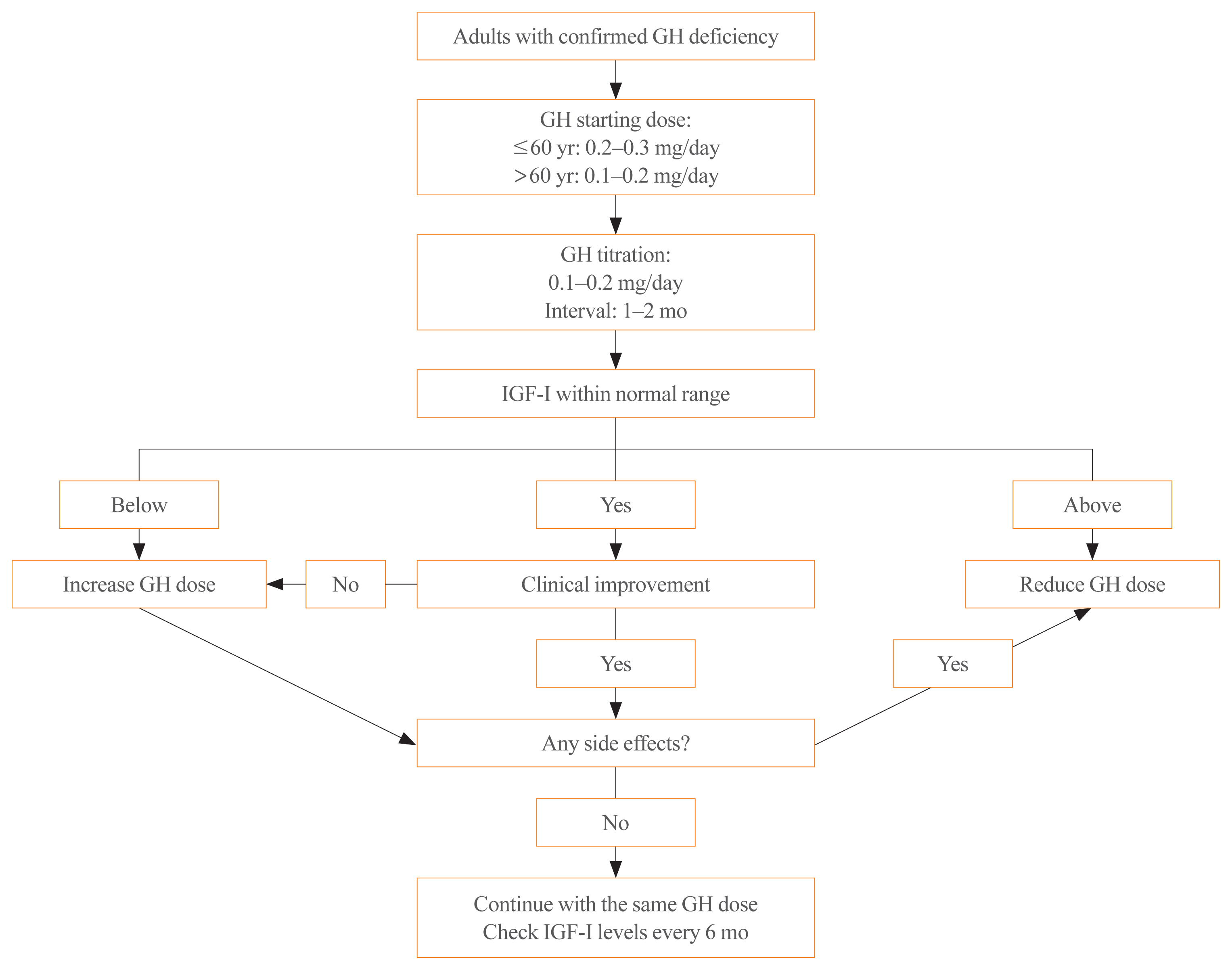
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,520 View
- 429 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction of norditropin and sogroya in patients with growth hormone deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Obieda Altobaishat, Mohamed Abouzid, Mostafa Hossam El Din Moawad, Abdulrahman Sharaf, Yazan Al-Ajlouni, Tungki Pratama Umar, Abdallah Bani-salameh, Mohammad Tanashat, Omar Abdullah Bataineh, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

Original Articles
- Impact of Serum Adiponectin Concentration on Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Chul Sik Kim, Ju Ri Park, Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Ohk Hyun Ryu, Seong Jin Lee, Eun Gyung Hong, Doo Man Kim, Jae Myung Yoo, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):31-38. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.31
- 2,089 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Increased cardiovascular events, which is the leading cause of death in type 2 diabetic patients, are mainly caused by accelerated atherosclerosis. Adiponectin has been suggested as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in cross-sectional studies. However, little is known about the impact of adiponectin on the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of early adiponectin levels on the progression of carotid atherosclerosis. METHODS: From March 2009, 150 patients with type 2 diabetes were consecutively enrolled in our affiliated outpatient clinic. Anthropometric and biochemical data, including adiponectin levels, were measured in each participant. We measured the carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) at baseline and at 1-year follow-up (n = 111). Then, we prospectively studied the relationship between the serum adiponectin levels and the progression of CIMT for 1 year. RESULTS: Adiponectin levels negatively correlated with CIMT (r = -0.219, P = 0.015). Moreover, mean progression of CIMT was 0.016 +/- 0.040 mm. However, there was no correlation between adiponectin levels and the progression of CIMT within 1-year follow-up period (r = -0.156, P = 0.080). Age (beta = 0.556, P = 0.004), LDL cholesterol (beta = 0.276, P = 0.042), and A1C (beta = 0.309, P = 0.038) were found to be independent risk factors for CIMT. However, A1C (beta = 0.311, P = 0.042) was found to be the only independent risk factor for the progression of CIMT. CONCLUSION: In our study, adiponectin levels were negatively associated with CIMT. However, it did not affect the progression of CIMT at 1-year follow-up. Overall glycemic control is the most important factor in the progression of CIMT in patients with type 2 diabetes.

- Six Cases of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia That Were Due to 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase Deficiency.
- Dong Hoon Shin, Sung Hoon Yu, Young Min Choi, Jung Gu Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(2):109-115. Published online June 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.109
- 1,969 View
- 29 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency is a rare phenotype of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and this is characterized by hyporeninemic hypertension, primary amenorrhea and abnormality of the secondary sexual characteristics (pseudohermaphroditism in men). This type of CAH is usually misdiagnosed at first as mineralocorticoid induced hypertension with primary aldosteronism, but primary amenorrhea with deficient sex hormone is a clue for making the correct diagnosis. The authors experienced 6 cases of 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency in patients who ranged from 15 to 42 years of age. 4 cases were diagnosed according to the investigation of their mineralocorticoid-induced hypertension and 2 cases their primary amenorrhea and sexual infantilism. All of them had hypokalemia, hyporeninemic hypertension and an atrophied uterus and ovaries. In the genotypic male (46 XY), the testicles were atrophied in the abdominal cavity. The levels of cortisol, estrogen and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) were low, but the levels of progesterone and 11-deoxycorticosterone were high. Therefore, the diagnosis of 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency should be considered in female patients who present with both sexual infantilism and mineralocorticoid hypertension. We report on these cases with a brief review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Functional Identification of Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the CYP17A1 Gene Resulting in Combined 17α-Hydroxylase/17,20-Lyase Deficiency
Eun Yeong Mo, Ji-young Lee, Su Yeon Kim, Min Ji Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Seungok Lee, Je Ho Han, Sung-dae Moon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(3): 413. CrossRef - 17α-hydroxylase Deficiency Mimicking Hyperaldosteronism by Aldosterone-producing Adrenal Adenoma
Yun Kyung Cho, Hyeseon Oh, Sun-myoung Kang, Sujong An, Jin-Young Huh, Ji-Hyang Lee, Woo Je Lee
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2016; 91(2): 191. CrossRef
- Functional Identification of Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the CYP17A1 Gene Resulting in Combined 17α-Hydroxylase/17,20-Lyase Deficiency


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



